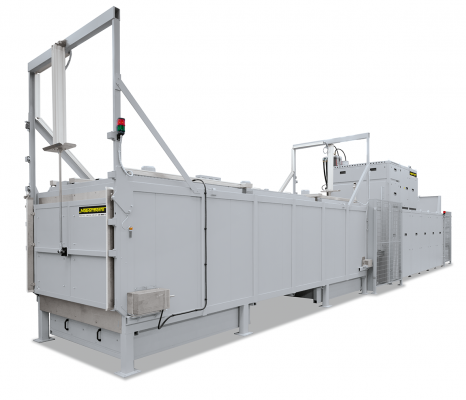
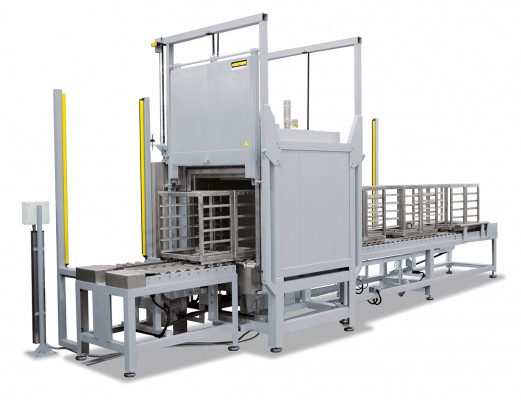
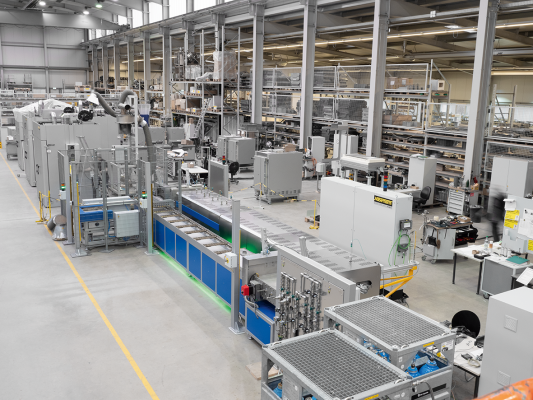
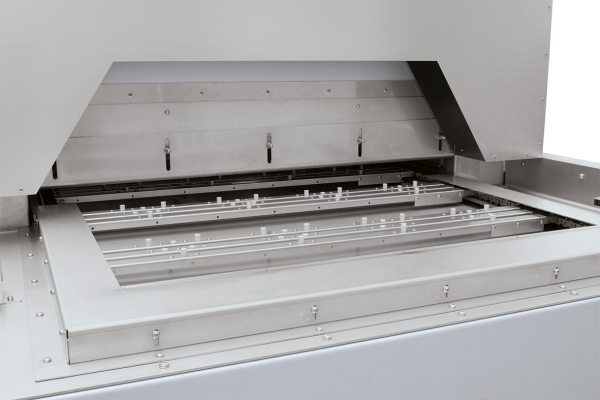
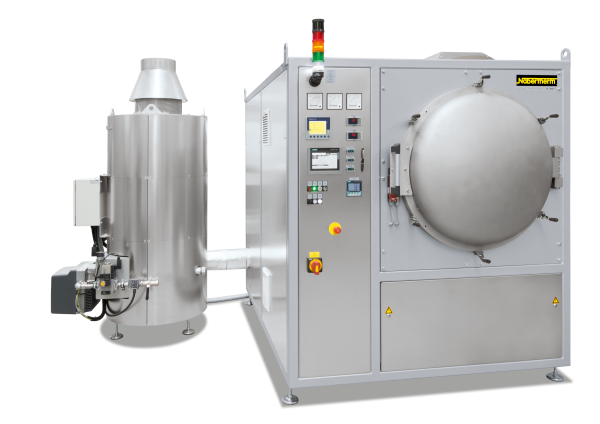
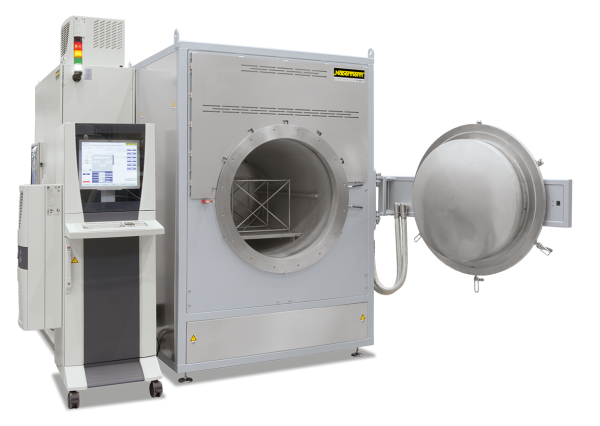
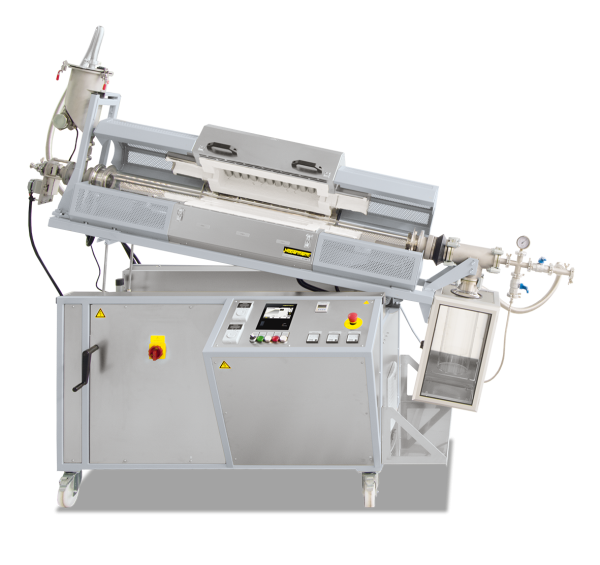
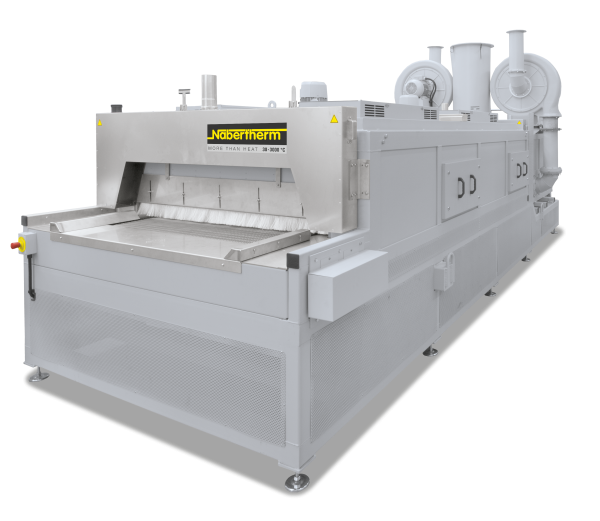
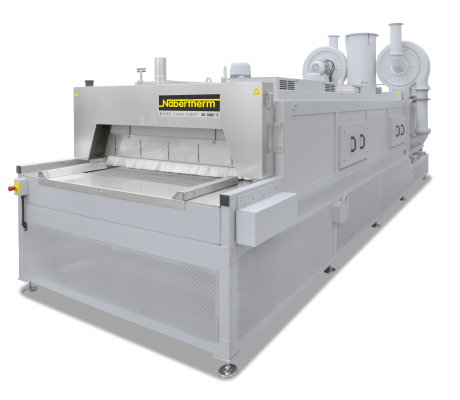
Continuous furnaces are the right choice for processes with fixed cycle times such as drying or preheating, curing, aging, vulcanisation or degassing. The furnaces are available for various temperatures up to a maximum of 1100 °C. The furnace design depends on the required throughput, the process requirements for heat treatment and the required cycle time.
The conveyor technology is tailored to the required working temperature, geometry and weight of the charge and to the requirements regarding available space and integration into the process chain. The conveyor speed and the number of control zones are defined by the process specifications.
Conveyor concepts
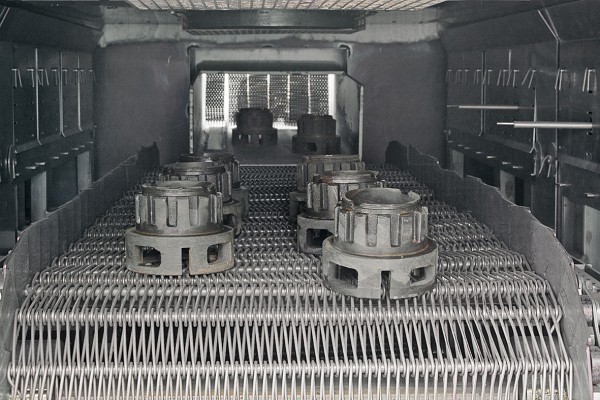
- Conveyor belt
- Metal conveyor belt with adjusted mesh gauges
- Drive chain
- Roller conveyors
- Paternoster
- Pusher-type
- Rotary hearth
Heating systems
- Electric heating, radiation or convection
- Direct or indirect gas-fired
- Infrared heating
- Heating with the use of external heat sources
Temperature cycles
- Control of working temperature across the whole length of the furnace, such as for drying or preheating
- Automatic control of a process curve applying defined heat-up, dwell and cooling time
- Heat treatment including a final quenching of the charge
Process atmosphere
- In air
- For processes with organic outgassings incl. mandatory safety technology according to EN 1539
- In non-flammable protective or reactive gases such as nitrogen, argon or forming gas
- In flammable protective or reactive gases such as hydrogen incl. the necessary safety technology
Basic configuration criteria
- Conveyor speed
- Temperature uniformity
- Operating temperature
- Process curve
- Work space width
- Charge weights
- Cycle time or throughput
- Length of charge and discharge zone
- Generated exhaust gases
- Specific industry standards such as AMS2750G, CQI-9, FDA etc.
- Other individual customer requirements